How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Algorithmic and Quantitative Trading
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has fundamentally reshaped modern financial markets. From institutional hedge funds to sophisticated retail traders, AI-driven trading systems now dominate decision-making processes, execution speed, and risk management. We explore how AI for trading works in practice, the models that drive profitable strategies, and why algorithmic trading powered by machine learning has become a structural advantage rather than an optional enhancement.
What AI for Trading Really Means in Modern Markets
AI for trading refers to the application of machine learning, deep learning, and data-driven algorithms to analyze financial markets, generate trading signals, manage risk, and execute trades with minimal human intervention.
Unlike traditional rule-based systems, AI trading models learn from historical and real-time data, adapt to changing market conditions, and continuously refine their predictions. This adaptive intelligence is the defining feature separating modern AI trading systems from legacy algorithmic strategies.
Key capabilities include:
- Pattern recognition across massive datasets
- Probabilistic forecasting of price movements
- Automated feature extraction from unstructured data
- Continuous model retraining based on new market information
Core AI Technologies Powering Algorithmic Trading
Machine Learning Models in Trading Systems
Machine learning is the backbone of AI-driven trading. Commonly deployed models include:
- Supervised learning for price prediction and signal classification
- Unsupervised learning for market regime detection and clustering
- Reinforcement learning for strategy optimization and execution decisions
Models such as Random Forests, Gradient Boosting Machines, and Support Vector Machines are widely used for structured market data like OHLCV and technical indicators.
Deep Learning for Complex Market Behavior
Deep learning models excel at capturing nonlinear relationships and temporal dependencies. In trading, they are used for:
- Time-series forecasting with LSTM and GRU networks
- High-frequency trading signal extraction
- Volatility modeling and tail-risk estimation
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are increasingly applied to transformed price data, while Transformers are emerging as state-of-the-art models for multi-asset prediction.
Data Sources That Give AI Trading Models an Edge
Structured Market Data
AI trading systems ingest vast quantities of structured data, including:
- Historical price and volume data
- Order book and tick-level data
- Derivatives data such as options chains and futures curves
This data forms the foundation for predictive modeling and backtesting.
Alternative and Unstructured Data
What differentiates elite AI trading systems is their use of alternative data:
- News feeds and earnings call transcripts
- Social media sentiment and market chatter
- Macroeconomic indicators and policy statements
- Satellite data and web traffic metrics
Natural Language Processing (NLP) models convert unstructured text into quantitative signals that influence trading decisions in real time.
AI-Driven Trading Strategies That Outperform
Predictive Alpha Generation
AI models identify subtle statistical inefficiencies that are invisible to traditional analysis. These inefficiencies are converted into alpha-generating signals across equities, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
Unlike static indicators, AI-driven alpha evolves with market conditions, reducing signal decay.
Statistical Arbitrage and Market Neutral Strategies
AI excels at:
- Pair trading and basket arbitrage
- Mean reversion detection across correlated assets
- Regime-aware position sizing
Machine learning models dynamically adjust exposure based on volatility, liquidity, and correlation breakdowns.
High-Frequency and Low-Latency Trading
In high-frequency environments, AI models:
- Optimize order placement and execution timing
- Predict short-term order flow imbalance
- Reduce slippage and market impact
Reinforcement learning agents continuously learn the most efficient execution policies under changing microstructure conditions.
Risk Management Enhanced by Artificial Intelligence
Real-Time Risk Monitoring
AI systems monitor portfolio risk continuously, not periodically. They detect:
- Volatility spikes
- Correlation regime shifts
- Liquidity deterioration
This enables proactive risk reduction rather than reactive loss mitigation.
Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis
Machine learning models simulate thousands of market scenarios, including extreme tail events. This improves:
- Drawdown control
- Capital allocation efficiency
- Portfolio resilience under stress
AI-based risk engines outperform traditional VaR models by capturing nonlinear dependencies.
AI for Retail Algorithmic Trading: Democratization of Quant Finance
AI has significantly lowered the barrier to entry for retail traders. Cloud computing, open-source libraries, and broker APIs now enable individuals to deploy institutional-grade strategies.
Key enablers include:
- Python-based trading frameworks
- Pre-trained machine learning models
- Low-latency API access to global markets
- Affordable cloud infrastructure for backtesting
Retail traders increasingly use AI to automate strategy development, reduce emotional bias, and scale trading operations efficiently.
Infrastructure Required for AI Trading Systems
Computing and Architecture
Successful AI trading systems rely on robust infrastructure:
- Cloud-based GPUs and TPUs for model training
- Low-latency servers for live execution
- Distributed data pipelines for real-time ingestion
Scalability and reliability are critical, especially for multi-asset strategies.
Model Lifecycle Management
AI trading requires disciplined model governance:
- Continuous retraining and validation
- Drift detection and performance monitoring
- Version control for models and data
Without rigorous lifecycle management, AI models degrade rapidly in live markets.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations in AI Trading
As AI trading becomes widespread, regulatory scrutiny has increased. Key considerations include:
- Model transparency and explainability
- Market manipulation and fairness concerns
- Data privacy and compliance
Institutions now deploy explainable AI (XAI) techniques to satisfy regulators while maintaining predictive power.
Future Trends in AI for Trading
Autonomous Trading Agents
The next evolution involves fully autonomous agents capable of:
- Strategy discovery without human-defined rules
- Dynamic capital allocation across markets
- Self-correction after losses
These systems blur the line between research, execution, and risk management.
Multimodal AI Models
Future trading systems integrate price data, text, images, and macro signals into unified models. This holistic market understanding significantly improves forecast accuracy.
AI-Human Hybrid Decision Systems
Rather than replacing traders, AI increasingly augments decision-making, providing probabilistic insights while humans define strategic objectives and constraints.
AI Trading System Architecture Overview
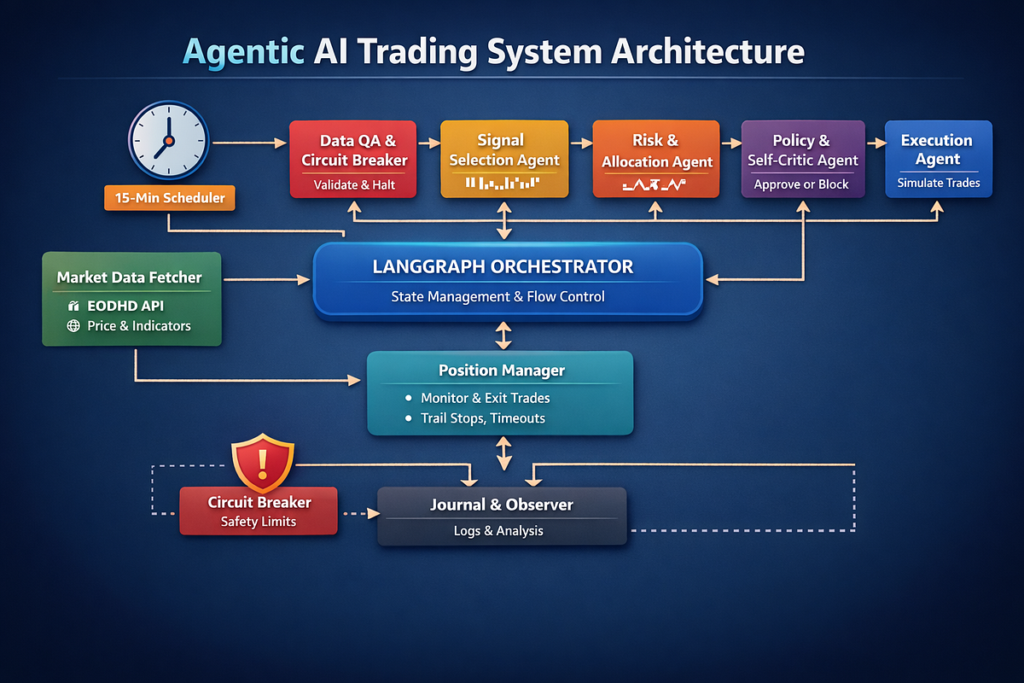
Why AI for Trading Is a Structural Advantage
AI for trading is no longer experimental. It is embedded in the core of modern financial markets, delivering superior speed, adaptability, and analytical depth. Firms and traders that fail to adopt AI-driven strategies face persistent competitive disadvantage.
By combining advanced machine learning models, diverse data sources, and robust infrastructure, AI trading systems consistently outperform static, rule-based approaches. As markets grow more complex and data-rich, artificial intelligence remains the most effective tool for extracting sustainable trading edge.
Final Perspective
AI has redefined how trading strategies are designed, executed, and managed. From predictive analytics to autonomous execution, AI-driven algorithmic trading represents the most powerful evolution in quantitative finance. The competitive frontier now belongs to those who master data, models, and intelligent automation at scale.